I remember teachers asking the question, “What is the largest human organ?” in class many years ago, and most kids shouted out incorrect guesses, like the stomach or the brain. While the largest internal human organ is the liver, by now we should all know that the skin is the actual largest organ. There has been a lot of research into 3D printed skin, which is great news for burn victims, those suffering from skin disease, and those who want to hold on to to their youth. Bioengineers have been looking into different 3D printing techniques to produce synthetic human skin for years, as it could also help with reconstructive surgery. A research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) in South Korea, no stranger to 3D printing research, has just introduced an innovative single-step process for 3D bioprinting synthetic skin.
The POSTECH team recently published their work on the breakthrough process in a research paper, titled “Direct 3D cell-printing of human skin with functional transwell system,” in the Biofabrication journal; co-authors include Byoung Soo-Kim, Ge Gao, Jung-Seob Lee, and lead author Dong-Woo Cho, who was also part of a team in 2014 that developed a 3D printed scaffolding implant that was used to help realign a patient’s eyes after a tumor removal.
The paper’s abstract reads, “In this paper, we present a new 3D cell-printing strategy for engineering a 3D human skin model with a functional transwell system in a single-step process. A hybrid 3D cell-printing system was developed, allowing for the use of extrusion and inkjet modules at the same time. We began by revealing the significance of each module in engineering human skin models; by using the extrusion-dispensing module, we engineered a collagen-based construct with polycaprolactone (PCL) mesh that prevented the contraction of collagen during tissue maturation; the inkjet-based dispensing module was used to uniformly distribute keratinocytes. Taking these features together, we engineered a human skin model with a functional transwell system; the transwell system and fibroblast-populated dermis were consecutively fabricated by using the extrusion modules. Following this process, keratinocytes were uniformly distributed onto the engineered dermis by the inkjet module. Our transwell system indicates a supportive 3D construct composed of PCL, enabling the maturation of a skin model without the aid of commercial transwell inserts. This skin model revealed favorable biological characteristics that included a stabilized fibroblast-stretched dermis and stratified epidermis layers after 14 days. It was also observed that a 50 times reduction in cost was achieved and 10 times less medium was used than in a conventional culture. Collectively, because this single-step process opens up chances for versatile designs, we envision that our cell-printing strategy could provide an attractive platform in engineering various human skin models.”
The POSTECH team’s process is faster and less expensive then current methods, and can make a 3D synthetic skin structure in just one process, as opposed to other processes that use multiple steps.
“Although several approaches have been explored for developing biomimetic human skin models, the present skin models, which are still based on multistep production methods using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chips and commercial cell culture inserts, could be limited in making a versatile design that facilitates the development of various functional human skin models,” explained Cho.

The team developed a hybrid system to print the synthetic skin in one process; it simultaneously uses both extrusion and inkjet modules on the printer head. The extrusion module is used to engineer a scaffold, using a collagen-based material with a polycaprolactone (PCL) membrane, which has also been used to 3D print bones.
Cho explained, ““PCL is a biodegradable polyester that prevents collagen’s contraction during tissue maturation.”
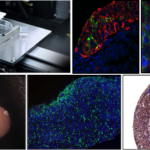
At the same time the extrusion module is making the scaffolding, the inkjet system uniformly distributes keratinocytes, which are the main type of cell found in the outermost layer of skin, onto the scaffolding. The team said that two weeks after the printing process, their synthetic skin displayed several good biological characteristics, such as good stretchability and a layered structure.
“Significantly, our new method is around 50 times cheaper than alternative methods, and requires 10 times less base material. In this regard, [this] 3D cell-printing technique could establish a new era for advanced skin models,” Cho said.
Discuss in the POSTECH forum at 3DPB.com.
[Source: The Engineer]
If you're looking to get architectural 3D animation in the USA, our service provides an exceptional way to bring your architectural concepts to life through dynamic, immersive visuals. Through our platform, you can easily request high-quality 3D animations that showcase your designs in motion, offering a detailed view of your project from multiple angles and perspectives. Whether it's for a real estate development, a commercial building, or an urban planning project, our expert team ensures that every detail is captured in a visually compelling animation.
Through our website, you can seamlessly get architectural 3D animation tailored to your project’s specific needs. With our help, you can offer potential clients or investors an engaging experience that goes beyond static images. By integrating CGI animations with real-world settings, lighting, and textures, our team creates a lifelike experience that allows your audience to interact with your project as though it were already built. This service is perfect for presenting complex designs in a clear, visually attractive way that stands out in the competitive architectural market.